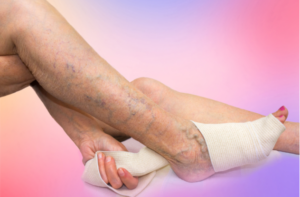
- Dull aching
- Cramping or heaviness in the legs
- Itching and tingling
- Pain that gets worse when standing
- Pain that gets better when legs are raised
- Skin changes in the legs such as cracked or discolored skin, redness, or leg ulcers
What You Can Do to Manage Venous Insufficiency
We mentioned that venous insufficiency tends to worsen over time. However, there are actions that can be taken to slow this progression or even halt it. These include:
Increase Activity Levels
The veins in the legs are helped by the muscles in the calves. This knowledge can motivate lifestyle changes that include an increase in physical activity. Doctors typically advise patients to engage in low-impact exercise to help support vein health. Running is acceptable, but walking or biking is just as beneficial. The point is to work the calves to help blood move properly through the veins. Even when sitting at a desk job, minor exercises like raising the heels can be performed. It is also necessary to get up and walk for a few minutes every few hours. Every hour, simply stand up and sit back down a few times. This works the calves and increases heart rate just enough to improve circulation.
Wear Compression Garments
Compression garments can be worn while working out or when standing for long periods. The flexible fabric gently presses on the calf muscles to increase support of the veins. When wearing compression socks, blood tends to move more efficiently out of the legs.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Weight is a contributing factor to venous insufficiency because the heavier a person is, the more stress their legs and veins are under. In many cases, patients who are overweight also lead relatively sedentary lives, so they have two or more significant risk factors affecting their risk of venous insufficiency. Weight loss need not happen at an accelerated rate to improve the prognosis of vein health. Reducing the intake of processed and sugary foods and increasing physical activity and water intake are two great ways to get moving in a healthier direction.
Elevate the Legs
The problem with venous insufficiency is that the legs are not sending blood upward as they should. Blood is pooling in the veins. Elevating the legs by lying on the back and placing the legs at a 90-degree angle against a wall or propped on a chair helps move blood out of the swollen veins. Some studies suggest that lying like this before bed can help promote a better night’s sleep.
Avoid Salt
Salt, sodium, can cause water retention. The excess of fluid in the legs can exacerbate swelling in the veins and accelerate the ongoing weakening of the valves that are supposed to prevent blood from moving backward.
Venous insufficiency is a condition that can be managed well with the right care. To discuss the treatment options available at Metropolitan Vascular Institute in Waldorf, MD, contact us at (301) 374-8540.